Page 26 - DT 13-3.qxd
P. 26
22-26-Cyntia Galvão Gomes-Q8_6-7-8-Ivoclar.qxd 10/21/2023 5:47 PM Page 5
26 cosmetic section DENTAL TECHNOLOGY, JULY-SEPTEMBER 2023
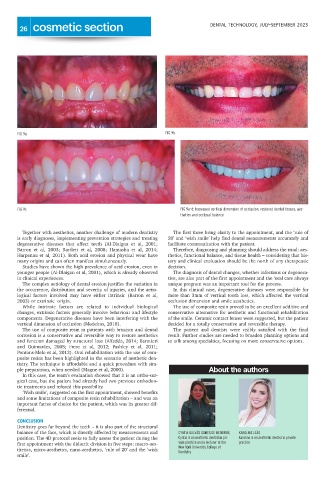
FIG 9a FIG 9b
FIG 9c FIG 9a-d: Increased vertical dimension of occlusion, restored dental tissues, aes-
thetics and occlusal balance
Together with aesthetics, another challenge of modern dentistry The first three bring clarity to the appointment, and the ‘rule of
is early diagnoses, implementing prevention strategies and treating 20’ and ‘wish smile’ help find dental measurements accurately and
degenerative diseases that affect teeth (Al-Dlaigan et al, 2001; facilitate communication with the patient.
Barron et al, 2003; Bartlett et al, 2008; Hamasha et al, 2014; Therefore, diagnosing and planning should address the triad: aes-
Harpenau et al, 2011). Both acid erosion and physical wear have thetics, functional balance, and tissue health – considering that his-
many origins and can often manifest simultaneously. tory and clinical evaluation should be the north of any therapeutic
Studies have shown the high prevalence of acid erosion, even in decision.
younger people (Al-Dlaigan et al, 2001), which is already observed The diagnosis of dental changes, whether infectious or degenera-
in clinical experiences. tive, are also part of the first appointment and the ‘oral care always
The complex aetiology of dental erosion justifies the variation in unique program was an important tool for the process.
the occurrence, distribution and severity of injuries, and the aetio- In this clinical case, degenerative diseases were responsible for
logical factors involved may have either intrinsic (Barron et al, more than 3mm of vertical tooth loss, which affected the vertical
2003) or extrinsic origin. occlusion dimension and smile aesthetics.
While intrinsic factors are related to individual biological The use of composite resin proved to be an excellent additive and
changes, extrinsic factors generally involve behaviour and lifestyle conservative alternative for aesthetic and functional rehabilitation
components. Degenerative diseases have been interfering with the of the smile. Ceramic contact lenses were suggested, but the patient
vertical dimension of occlusion (Medeiros, 2018). decided for a totally conservative and reversible therapy.
The use of composite resin in patients with bruxism and dental The patient and dentists were visibly satisfied with the final
corrosion is a conservative and reversible way to restore aesthetics result. Further studies are needed to broaden planning options and
and function damaged by structural loss (Alfadda, 2014; Baratieri to talk among specialties, focusing on more conservative options.
and Guimarães, 2008; Frese et al, 2012; Pashley et al, 2011;
Pontons-Melo et al, 2012). Oral rehabilitation with the use of com-
posite resins has been highlighted in the scenario of aesthetic den-
tistry. The technique is affordable and a quick procedure with sim-
ple preparation, when needed (Magne et al, 2000). About the authors
In this case, the team’s evaluation showed that it is an ortho-sur-
gical case, but the patient had already had two previous orthodon-
tic treatments and refused this possibility.
‘Wish smile’, suggested on the first appointment, showed benefits
and some limitations of composite resin rehabilitation – and was an
important factor of choice for the patient, which was its greater dif-
ferential.
CONCLUSION
Dentistry goes far beyond the teeth – it is also part of the structural
balance of the face, which is directly affected by measurements and CYNTIA GALVÃO GOMES DE MEDEIROS KAROLINE LEÃO
position. The 4D protocol seeks to fully assess the patient during the Cyntia is an aesthetic dentist in pri- Karoline is an aesthetic dentist in private
first appointment with the didactic division in five steps: macro-aes- vate practice and a lecturer at the practice
New York University College of
thetics, micro-aesthetics, nano-aesthetics, ‘rule of 20’ and the ‘wish
Dentistry
smile’.