Page 54 - DP Vol 21 No1_Neat
P. 54
IMPLANTOLOGY
A MINIMALLY INVASIVE IMMEDIATE
IMPLANT RESTORATION USING THE
EXOCAD SOFTWARE TOOLS
Dr. Jan Erik Jansohn
CASE REPORT
Dr. Jan Erik Jansohn, M.Sc., from Düsseldorf, demonstrates the
advantages of digital pre-planning with guided implant placement
for minimally invasive immediate restoration concepts using the
case study of this patient named Monique. The patient underwent
restoration of a free-end situation in the right maxilla from 13 to
17, using three implants with guided implantation and immediate
restoration through a fixed implant-supported long-term provisional
bridge.
INITIAL SITUATION
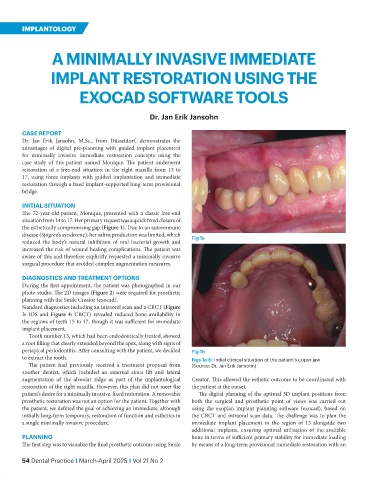
The 72-year-old patient, Monique, presented with a classic free-end
situation from 14 to 17. Her primary request was a quick fixed closure of
the esthetically compromising gap (Figure 1). Due to an autoimmune
disease (Sjögren’s syndrome), her saliva production was limited, which Fig 1a
reduced the body’s natural inhibition of oral bacterial growth and
increased the risk of wound healing complications. The patient was
aware of this and therefore explicitly requested a minimally invasive
surgical procedure that avoided complex augmentation measures.
DIAGNOSTICS AND TREATMENT OPTIONS
During the first appointment, the patient was photographed in our
photo studio. The 2D images (Figure 2) were required for prosthetic
planning with the Smile Creator (exocad).
Standard diagnostics including an intraoral scan and a CBCT (Figure
3: IOS and Figure 4: CBCT) revealed reduced bone availability in
the regions of teeth 15 to 17, though it was sufficient for immediate
implant placement.
Tooth number 13, which had been endodontically treated, showed
a root filling that clearly extended beyond the apex, along with signs of
periapical periodontitis. After consulting with the patient, we decided Fig 1b
to extract the tooth. Figs 1a-b: Initial clinical situation of the patient‘s upper jaw
The patient had previously received a treatment proposal from (Source: Dr. Jan Erik Jansohn)
another dentist, which included an external sinus lift and lateral
augmentation of the alveolar ridge as part of the implantological Creator. This allowed the esthetic outcome to be coordinated with
restoration of the right maxilla. However, this plan did not meet the the patient at the outset.
patient’s desire for a minimally invasive, fixed restoration. A removable The digital planning of the optimal 3D implant positions from
prosthetic restoration was not an option for the patient. Together with both the surgical and prosthetic point of views was carried out
the patient, we defined the goal of achieving an immediate, although using the exoplan implant planning software (exocad), based on
initially long-term temporary, restoration of function and esthetics in the CBCT and intraoral scan data. The challenge was to plan the
a single minimally invasive procedure. immediate implant placement in the region of 13 alongside two
additional implants, ensuring optimal utilization of the available
PLANNING bone in terms of sufficient primary stability for immediate loading
The first step was to visualize the final prosthetic outcome using Smile by means of a long-term provisional immediate restoration with an
54 Dental Practice I March-April 2025 I Vol 21 No 2